Oversized Load vs Wide Load
Key Differences and Appropriate Use Cases
Overweight freight Shipping Canada
When it comes to heavy haul transport, the terms “oversized load” and “wide load” often come into play. But what do these terms really mean, and how do they differ?
Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone involved in logistics services, construction, or trucking services.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the world of specialized trucking, exploring their definitions, legal regulations, common use cases, and key differences.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of shipping over dimensional freight. When and how to use oversized or wide loads effectively.
Wide load trucking Canada
Understanding Oversized Loads
Hauling Wide Loads and Oversize Freight
Wide Load vs Oversize
In the world of highway travel, wide loads often find themselves in a unique category, primarily because they stretch beyond the standard legal width limit of 8.5 feet.
This dimension is more than just a number; it’s a boundary that dictates the need for specialized transportation solutions. Enter oversize loads, which take the concept of “big” to another level by exceeding legal limits not just in width, but in length, height, or weight as well.
The distinction here is crucial, as wide loads necessitate the use of specific equipment for transport, such as flatbed trailers, to ensure they can navigate the roads safely and efficiently.
This isn’t just about moving goods; it’s about understanding the intricacies of logistics and the importance of adhering to legal standards to keep our highways safe and functional.
Definition and Characteristics
It refers to cargo that exceeds the standard legal limits for weight, height, length, or width. These oversized heavy haul loads are typically larger than the dimensions allowed on flatbed trucks travelling on public roads without special oversize overweight permits and escort vehicles.
They both can vary significantly in size and shape. This can include heavy machinery transport, construction equipment transportation, and even pre-fabricated structures.
The key characteristic is that it exceeds the legal limits set by transportation authorities is the following.
- 12 feet, 6″ high
- 14 feet, 6″ in wide
- 52,000 lbs
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Transporting oversize and overweight freight is subject to strict legal regulations in most countries. These Canadian heavy haul regulations aim to ensure the safety of both the cargo and other road users.
Key legal requirements include:
Weight Limits: Most regions have strict weight limits for oversized loads to prevent excessive strain on roadways and bridges.
Dimensional Limits: In addition to weight, there are limits on the dimensions of wideload transport. This includes restrictions on width, height, and length.
Common Types of Oversized Loads
It can encompass a wide range of cargo, including:
- Machinery and Equipment: This category includes large construction equipment, industrial machinery, and oversized vehicles.
- Building Materials: Oversized loads can also consist of prefabricated building components such as trusses, beams, and precast concrete sections.
Challenges and Risks
Several are involved, including:
Road Safety: This kind of specialised flatbed trucking can obstruct traffic and require specialized handling to navigate safely through intersections and narrow roads.
Infrastructure Considerations: The weight of oversized loads can damage roads, bridges, and other infrastructure if not properly managed.
Definition and Characteristics
Now, let’s turn our attention to wide loads. A wide load, as the name suggests, is cargo that exceeds the standard width limitations set by transportation authorities.
Unlike oversized loads, which can be oversized in multiple dimensions, wide loads specifically refer to cargo that is wider than permitted.
Wide load transportation is also subject to stringent legal requirements, including:
- Maximum Width Allowances: Regulations dictate the maximum width allowed for wide loads, typically requiring wide load permits and safety precautions when exceeding these limits.
- Markings and Escorts: Wide loads often require specialized markings and escort vehicles to alert other road users and ensure safe transport.
Common Types of Wide Loads
Modular Homes: Transporting modular homes, which are often wider than standard cargo, falls under the category of wide loads.
Wind Turbine Blades: These exceptionally long and wide components require specialized transport due to their dimensions.
Heavy haul transportation presents its own set of challenges and risks, including:
- Traffic Disruptions: Wide loads can slow down traffic significantly and require careful planning to minimize disruptions.
- Clearing Obstacles: Navigating through narrow roads and obstacles like traffic signals and signs can be particularly challenging for wide loads.
Key Differences of Oversized Load vs Wide Load
Let’s explore the key differences between them:
Size and Dimensions
Oversized loads can exceed legal limits in multiple dimensions (weight, width, height, length), while wide loads specifically pertain to width.
Legal Requirements
Oversized loads have legal restrictions on multiple dimensions, whereas wide loads primarily concern width.
Types of Cargo
Cargo include heavy machinery and building materials, while wide loads often involve wide but not necessarily heavy cargo.
Transportation Methods
It may require specialized trailers or equipment, while wide loads often involve widening trailers or escort vehicles to accommodate width.
Impact on Roadways and Infrastructure
– Oversized loads, due to their weight, may have a more significant impact on roadways and infrastructure compared to wide loads, which primarily affect road width.
Appropriate Use Cases for Oversized Loads
Now that we understand the nuances of oversized loads, let’s explore their appropriate use cases:
Industries and Sectors That Commonly Use Oversized Loads
Construction: This method frequently used to transport heavy construction equipment and materials to job sites.
Manufacturing: Large machinery and equipment used in manufacturing often require oversized load transportation.
Bridge Construction: Transporting bridge sections and support beams as oversized loads reduced construction time significantly.
Wind Farm Installation: Crucial for transporting wind turbine components to remote wind farm sites efficiently.
Housing: Modular homes and prefabricated structures often require wide load transportation to reach their destinations.
Renewable Energy: Wind turbine blades and tower sections are examples of wide loads used in the renewable energy sector.
Benefits of Wide Load Transport
Reduced Disassembly: Wide load transportation allows for the transport of large structures without disassembling them, saving time and money.
Minimal Site Alterations: In some cases, wide load transportation can eliminate the need for extensive alterations to accommodate large structures.
Here are a couple of instances where wide loads were instrumental:
Modular Home Delivery: Transporting entire modular homes as wide loads reduced construction time and on-site labor costs.
Wind Energy Expansion: Wide load transportation facilitated the expansion of wind energy projects by efficiently delivering oversized wind turbine components.
Choosing Between Oversized and Wide Loads
Let’s explore how to make the right decision:
Cargo Specifications: Consider the size, weight, and dimensions of the cargo.
Route and Destination: Evaluate the route’s suitability for the cargo’s dimensions and any potential obstacles.
Budget Constraints: Compare the costs associated with oversized and wide load transportation.
Let’s examine two scenarios where the choice between oversized and wide load transportation had a significant impact:
Manufacturing Facility Relocation: Choosing oversized load transportation enabled the efficient relocation of an entire manufacturing facility, minimizing downtime.
Historic Monument Transport: Wide load transportation was selected to transport a delicate historic monument without disassembly, preserving its integrity.
Safety and Risk Mitigation Strategies
Ensuring the safety of oversized and wide load transportation is paramount. Let’s explore some strategies to mitigate risks:
– Implement thorough safety measures, including proper signaling, lighting, and escort vehicles.
– Conduct regular inspections to identify and address potential issues before they become safety hazards.
– Work closely with transportation authorities to assess the impact of oversized and wide loads on infrastructure.
– Invest in infrastructure upgrades, such as reinforced bridges and road maintenance, where necessary.
Emergency Response Plans
– Develop comprehensive emergency response plans to address accidents or road closures quickly and efficiently.
Compliance with Regulations
– Stay up-to-date with evolving regulations and ensure full compliance to avoid legal complications.
– Keep an eye on regulatory changes that may impact the transportation of oversized and wide loads.
Whether you’re involved in construction logistics, manufacturing, or any industry requiring large cargo transportation, choosing between oversized and wide loads can significantly impact project success.
By staying compliant with regulations and prioritizing safety, you can navigate the challenges of transporting these specialized loads successfully.
In the ever-evolving landscape of transportation, the choices you make today will shape the future of oversized and wide load logistics.
Be prepared to adapt to rules for oversize heavy haul with new technologies, regulations, and environmental considerations as you continue to transport oversized and wide loads efficiently and responsibly.
The Weight and Dimension Limitations as per the Highway Traffic Act (HTA)
Whenever a vehicle’s dimensions or weight exceed the standard limits established by legislation, it is mandatory to obtain an oversize/overweight permit.
Below, we provide a breakdown of the weight and dimension restrictions specified in the HTA. Additional details can be found in the relevant sections of the HTA.
In situations where a movement surpasses the allowable limits outlined in the HTA, it’s advisable to explore alternative modes of transportation, such as rail, air, or water.
Maximum Width:
The maximum allowable width for a vehicle, including its load, is 2.6 meters.
Exceptions:
– Raw forest products (while en route) may have a width of up to 2.8 meters.
– Road service vehicles, as defined in Part X of the HTA, and such vehicles when traveling to and from a maintenance site or repair center, have no specified width limit.
– Loose fodder, including rectangular and round bales of hay, do not have a specified width limit.
Maximum Length (Single Vehicle):
A single vehicle, including its load, is permitted to have a maximum length of 12.5 meters.
Exceptions:
– This limitation does not apply to fire apparatus, semi-trailers, or articulated buses.
Maximum Length (Semi-trailer)
The length of a semi-trailer, including its load, must not exceed 16.15 meters (for SPIF) or 14.65 meters (for NON-SPIF, which stands for Safe, Productive, Infrastructure-Friendly).
Definition of Semi-trailer
A semi-trailer refers to a vehicle that is towed by another vehicle and is designed and used in such a way that a substantial part of its weight and load rests on, or is carried by, the other vehicle or a trailer converter dolly through a fifth wheel assembly.
It’s important to note that any extension in length caused by auxiliary equipment or machinery not intended for carrying a load is not included in this measurement.
Maximum Length (Combination of Vehicles)
The total length of a combination of vehicles and their oversize heavy haul loads should not exceed 23 meters.
Maximum Height
The combined height of a vehicle and its load must not exceed 4.15 meters.
Maximum Weight
The allowable weight limits are determined based on axle configurations and spacings. If the axle and/or gross vehicle weight exceeds the limits established by the HTA, an oversize/overweight permit is mandatory.
For detailed information regarding weight and dimensions, please refer to e-Laws: Highway Traffic Act Regulation 413/05 – Vehicle Weights and Dimensions, which focuses on safe, productive, and infrastructure-friendly vehicles.
Implements of Husbandry:
Oversize/overweight farm machinery, farm tractors, and self-propelled implements of husbandry (SPIH) carried on a plated motor vehicle or plated trailer drawn by a motor vehicle require an oversize/overweight permit.
It’s important to note that oversize loose fodder, such as hay bales, does not require a permit in accordance with HTA 109(2)
REDUCIBLE LOAD OVERWEIGHT POLICY
Producers or shippers are eligible to enter into agreements to operate wide load trucks which exceed the weights and/or dimensions identified in the Commercial Transport Regulations (CTR) when carrying reducible loads using vehicle configurations depicted in the Appendices to the CTR, and under the following conditions:
- The commodity must be capable of being hauled using vehicle combinations at legal weights and dimensions as identified in the CTR,
- The haul proponent is responsible for all studies as may be required to confirm:
- – the proposed vehicle configuration complies with recognized vehicle dynamics performance and safety thresholds at the requested weights, and
- – bridge capacities and any upgrades, if necessary to accommodate the haul vehicles at the requested weights,
- The haul proponent will be responsible for paying any costs associated with upgrading infrastructure to accommodate the haul,
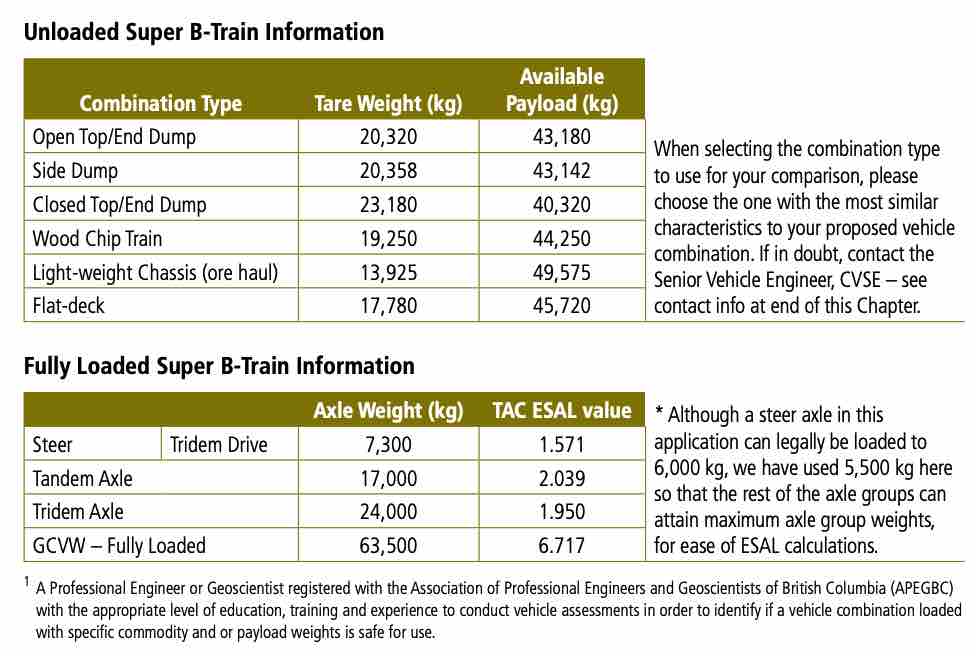
- The haul must generate a minimum of 5% reduction in Equivalent Single Axle Loadings (ESAL) when compared with the ESAL count which would be generated by the haul using a comparable Super B-train at legal weights and dimensions, according to the process outlined in section 6.5.1.
- Ifthehaulisapproved,theshipperwillberequiredtoensurethatanycarrieroperating pursuant to this agreement will:
- – comply with any pilot car requirements or other travel conditions resulting from the approved dimensions of the configuration and load (see Form CVSE1000),
- – implement a system for monitoring axle and gross vehicle weights, and make the vehicle weight information available to Ministry staff as required to audit compliance,
- – develop, document and demonstrate a driver training and monitoring program which is specific to the haul,
- – install electronic technology, including electronic driver logs, speed monitoring for each driver and vehicle on the haul, and
- – maintain a “Satisfactory” rating under the National Safety Code, and
- If the vehicles operate on highways which have inspection stations which are part of the Weigh2Go network, all vehicles operating pursuant to the agreement must be registered and maintain participation in the Weigh2Go program.
Application
The program considers applications to haul reducible loads at weights higher than legal 63,500kg and at overall lengths up to 27.5 m. The program is based on the assumption that the proponent already has the option and the ability to move the commodity at legal weights and dimension without any Commercial
Transport permit fees or additional analysis . Thus all haul costs are determined in comparison with a legal haul option, and all additional assessment and infrastructure costs are borne by the applicant.
REDUCIBLE LOAD OVERWEIGHT POLICY CANADA
All routes must be reviewed to assess whether bridges and pavements can accommodate the bulk haul. Any costs for work done by consultants as may be required to review bridge or pavement capacities will be paid by the haul proponent.
All vehicles must be safe to operate on the proposed route. Any new configurations or weight/dimension changes to existing configurations must be assessed to confirm they comply with recognized vehicle dynamics performance and safety thresholds. Any costs for work done by consultants to conduct the assessments will be paid by the haul proponent.
The proposed haul must generate an ESAL count which is at least 5% less than the ESAL count which would be generated if the haul occurred with the comparable legal B-train configuration.
An additional layer of analysis is required for safety considerations related to the transport of bulk liquids (tankers). Please consult with the Senior Vehicle Engineer, CVSE before initiating such a proposal; contact information can be found in the last pages in the downloadable heavy haul overweight permits pdf found from the button below.
This ESAL comparison must be conducted and signed off by a Qualified Professional , and will be calculated by comparing the ESAL’s which would be generated to move one million tonnes of payload using a standard ‘Super B Train’ (8-axle B Train) combination, with tare weights as shown below, to the ESAL’s generated by moving one million tonnes of payload using your proposed vehicle combination.
 <
<

Author & Chief Executive Officer at Paige Logistics Ltd. → Experienced Operations Manager with a demonstrated history of working in the Transportation, Shipping, Trucking and the Railroad Industry.
Related Posts

China is considered one of Canada’s leading merchandise trading partners and is an important supplier for Canadian businesses.

Clutch Awards 2023 Global Leader In Shipping
Clutch Global Top B2B Leader Awards 2022 names Paige Logistics among the Top Global B2B Shipping Companies and the top in Canada for container shipping, rail freight, flatbed trucking and freight forwarding.

agility & efficiency Understanding The Conestoga Trailer Click for best Price Benefits of Conestoga Trailer + 0 Deliveries 0 Happy

What Are DAP Incoterms Agreements? Let’s explore what it means to be a buyer or a seller in a DAP (delivery at place) Incoterms arrangement.

Finding a Top Shipping Logistics Company Canada
When it comes to choosing a shipping logistics services provider in Canada, it’s essential to select a company that can meet the specific needs of your business. The right provider like award winning Paige Logistics who can streamline the shipping logistics in your operations, provide dedicated transport services, save you money and ensure that your products are delivered to your customers on time and in perfect condition.


